Implementing Logistic Regression for Predicting if a Tumor is Malignant or Benign (From Scratch)
Implementing Logistic Regression for Predicting if a Tumor is Malignant or Benign (From Scratch)
Introduction
Bellow is my notebook from Kaggle for my project on implementing Logistic Regression from scratch for Predicting if a Tumor is Malignant or Benign and comparing it to scikit-learn predefined one.
Enjoy!
Notebook
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed
# It is defined by the kaggle/python Docker image: https://github.com/kaggle/docker-python
# For example, here's several helpful packages to load
import numpy as np # linear algebra
import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)
# Input data files are available in the read-only "../input/" directory
# For example, running this (by clicking run or pressing Shift+Enter) will list all files under the input directory
import os
for dirname, _, filenames in os.walk('/kaggle/input'):
for filename in filenames:
print(os.path.join(dirname, filename))
# You can write up to 20GB to the current directory (/kaggle/working/) that gets preserved as output when you create a version using "Save & Run All"
# You can also write temporary files to /kaggle/temp/, but they won't be saved outside of the current session
1
/kaggle/input/breast-cancer-wisconsin-data/data.csv
Overview
In this notebook i will predict if a Tumor is Malignant or Benign using logistic regression. i will implement everything from scratch then compare my results to a predefined algorithm in scikit learn.
Dataset
first i will load and explore the dataset. i’m working on Breast Cancer Wisconsin (Diagnostic) Data Set on Kaggle
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/uciml/breast-cancer-wisconsin-data
1
2
df = pd.read_csv("/kaggle/input/breast-cancer-wisconsin-data/data.csv")
df.head()
| id | diagnosis | radius_mean | texture_mean | perimeter_mean | area_mean | smoothness_mean | compactness_mean | concavity_mean | concave points_mean | ... | texture_worst | perimeter_worst | area_worst | smoothness_worst | compactness_worst | concavity_worst | concave points_worst | symmetry_worst | fractal_dimension_worst | Unnamed: 32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 842302 | M | 17.99 | 10.38 | 122.80 | 1001.0 | 0.11840 | 0.27760 | 0.3001 | 0.14710 | ... | 17.33 | 184.60 | 2019.0 | 0.1622 | 0.6656 | 0.7119 | 0.2654 | 0.4601 | 0.11890 | NaN |
| 1 | 842517 | M | 20.57 | 17.77 | 132.90 | 1326.0 | 0.08474 | 0.07864 | 0.0869 | 0.07017 | ... | 23.41 | 158.80 | 1956.0 | 0.1238 | 0.1866 | 0.2416 | 0.1860 | 0.2750 | 0.08902 | NaN |
| 2 | 84300903 | M | 19.69 | 21.25 | 130.00 | 1203.0 | 0.10960 | 0.15990 | 0.1974 | 0.12790 | ... | 25.53 | 152.50 | 1709.0 | 0.1444 | 0.4245 | 0.4504 | 0.2430 | 0.3613 | 0.08758 | NaN |
| 3 | 84348301 | M | 11.42 | 20.38 | 77.58 | 386.1 | 0.14250 | 0.28390 | 0.2414 | 0.10520 | ... | 26.50 | 98.87 | 567.7 | 0.2098 | 0.8663 | 0.6869 | 0.2575 | 0.6638 | 0.17300 | NaN |
| 4 | 84358402 | M | 20.29 | 14.34 | 135.10 | 1297.0 | 0.10030 | 0.13280 | 0.1980 | 0.10430 | ... | 16.67 | 152.20 | 1575.0 | 0.1374 | 0.2050 | 0.4000 | 0.1625 | 0.2364 | 0.07678 | NaN |
5 rows × 33 columns
1
df.shape
1
(569, 33)
1
df.info()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 569 entries, 0 to 568
Data columns (total 33 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 id 569 non-null int64
1 diagnosis 569 non-null object
2 radius_mean 569 non-null float64
3 texture_mean 569 non-null float64
4 perimeter_mean 569 non-null float64
5 area_mean 569 non-null float64
6 smoothness_mean 569 non-null float64
7 compactness_mean 569 non-null float64
8 concavity_mean 569 non-null float64
9 concave points_mean 569 non-null float64
10 symmetry_mean 569 non-null float64
11 fractal_dimension_mean 569 non-null float64
12 radius_se 569 non-null float64
13 texture_se 569 non-null float64
14 perimeter_se 569 non-null float64
15 area_se 569 non-null float64
16 smoothness_se 569 non-null float64
17 compactness_se 569 non-null float64
18 concavity_se 569 non-null float64
19 concave points_se 569 non-null float64
20 symmetry_se 569 non-null float64
21 fractal_dimension_se 569 non-null float64
22 radius_worst 569 non-null float64
23 texture_worst 569 non-null float64
24 perimeter_worst 569 non-null float64
25 area_worst 569 non-null float64
26 smoothness_worst 569 non-null float64
27 compactness_worst 569 non-null float64
28 concavity_worst 569 non-null float64
29 concave points_worst 569 non-null float64
30 symmetry_worst 569 non-null float64
31 fractal_dimension_worst 569 non-null float64
32 Unnamed: 32 0 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(31), int64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 146.8+ KB
1
df.describe()
| id | radius_mean | texture_mean | perimeter_mean | area_mean | smoothness_mean | compactness_mean | concavity_mean | concave points_mean | symmetry_mean | ... | texture_worst | perimeter_worst | area_worst | smoothness_worst | compactness_worst | concavity_worst | concave points_worst | symmetry_worst | fractal_dimension_worst | Unnamed: 32 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 5.690000e+02 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | ... | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 569.000000 | 0.0 |
| mean | 3.037183e+07 | 14.127292 | 19.289649 | 91.969033 | 654.889104 | 0.096360 | 0.104341 | 0.088799 | 0.048919 | 0.181162 | ... | 25.677223 | 107.261213 | 880.583128 | 0.132369 | 0.254265 | 0.272188 | 0.114606 | 0.290076 | 0.083946 | NaN |
| std | 1.250206e+08 | 3.524049 | 4.301036 | 24.298981 | 351.914129 | 0.014064 | 0.052813 | 0.079720 | 0.038803 | 0.027414 | ... | 6.146258 | 33.602542 | 569.356993 | 0.022832 | 0.157336 | 0.208624 | 0.065732 | 0.061867 | 0.018061 | NaN |
| min | 8.670000e+03 | 6.981000 | 9.710000 | 43.790000 | 143.500000 | 0.052630 | 0.019380 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.106000 | ... | 12.020000 | 50.410000 | 185.200000 | 0.071170 | 0.027290 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.156500 | 0.055040 | NaN |
| 25% | 8.692180e+05 | 11.700000 | 16.170000 | 75.170000 | 420.300000 | 0.086370 | 0.064920 | 0.029560 | 0.020310 | 0.161900 | ... | 21.080000 | 84.110000 | 515.300000 | 0.116600 | 0.147200 | 0.114500 | 0.064930 | 0.250400 | 0.071460 | NaN |
| 50% | 9.060240e+05 | 13.370000 | 18.840000 | 86.240000 | 551.100000 | 0.095870 | 0.092630 | 0.061540 | 0.033500 | 0.179200 | ... | 25.410000 | 97.660000 | 686.500000 | 0.131300 | 0.211900 | 0.226700 | 0.099930 | 0.282200 | 0.080040 | NaN |
| 75% | 8.813129e+06 | 15.780000 | 21.800000 | 104.100000 | 782.700000 | 0.105300 | 0.130400 | 0.130700 | 0.074000 | 0.195700 | ... | 29.720000 | 125.400000 | 1084.000000 | 0.146000 | 0.339100 | 0.382900 | 0.161400 | 0.317900 | 0.092080 | NaN |
| max | 9.113205e+08 | 28.110000 | 39.280000 | 188.500000 | 2501.000000 | 0.163400 | 0.345400 | 0.426800 | 0.201200 | 0.304000 | ... | 49.540000 | 251.200000 | 4254.000000 | 0.222600 | 1.058000 | 1.252000 | 0.291000 | 0.663800 | 0.207500 | NaN |
8 rows × 32 columns
1
list(df.columns.values)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
['id',
'diagnosis',
'radius_mean',
'texture_mean',
'perimeter_mean',
'area_mean',
'smoothness_mean',
'compactness_mean',
'concavity_mean',
'concave points_mean',
'symmetry_mean',
'fractal_dimension_mean',
'radius_se',
'texture_se',
'perimeter_se',
'area_se',
'smoothness_se',
'compactness_se',
'concavity_se',
'concave points_se',
'symmetry_se',
'fractal_dimension_se',
'radius_worst',
'texture_worst',
'perimeter_worst',
'area_worst',
'smoothness_worst',
'compactness_worst',
'concavity_worst',
'concave points_worst',
'symmetry_worst',
'fractal_dimension_worst',
'Unnamed: 32']
Here i noticed a column named ‘Unnamed: 32’ and there values are NaN
1
2
df.drop(["Unnamed: 32"], axis = 1, inplace=True)
list(df.columns.values)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
['id',
'diagnosis',
'radius_mean',
'texture_mean',
'perimeter_mean',
'area_mean',
'smoothness_mean',
'compactness_mean',
'concavity_mean',
'concave points_mean',
'symmetry_mean',
'fractal_dimension_mean',
'radius_se',
'texture_se',
'perimeter_se',
'area_se',
'smoothness_se',
'compactness_se',
'concavity_se',
'concave points_se',
'symmetry_se',
'fractal_dimension_se',
'radius_worst',
'texture_worst',
'perimeter_worst',
'area_worst',
'smoothness_worst',
'compactness_worst',
'concavity_worst',
'concave points_worst',
'symmetry_worst',
'fractal_dimension_worst']
Now we are talking :)
1
2
# Shuffle the data
data = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=42).reset_index(drop=True)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Calculate the number of samples for each set
train_size = int(0.8 * len(data))
test_size = int(0.2 * len(data))
# Split the dataset into training and test sets
train_data = data[:train_size] # training data (80%)
test_data = data[train_size:] # test data (20%)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Split the features and target for each set
X_train = train_data.drop('diagnosis', axis=1)
y_train = train_data['diagnosis']
X_test = test_data.drop('diagnosis', axis=1)
y_test = test_data['diagnosis']
y_train = y_train.map({'M': 1, 'B': 0}).astype(np.float64)
y_test = y_test.map({'M': 1, 'B': 0}).astype(np.float64)
1
2
print(f"Training set size: {len(X_train)} samples")
print(f"Test set size: {len(X_test)} samples")
1
2
Training set size: 455 samples
Test set size: 114 samples
Models
Logistic Regression from scratch
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class LogisticRegression :
def __init__(self, alpha=0.01, iterations=1000, scale=False):
self.alpha = alpha
self.iterations = iterations
self.scale = scale
self.w = None
self.b = None
self.cost_history = []
def scale_features(self,X):
"""Scale features using mean and std deviation (standardization)."""
self.mean = np.mean(X, axis=0)
self.std = np.std(X, axis=0)
return (X - self.mean) / self.std
def fit(self, X, y):
m = len(y) # Number of training examples
# Scale the features if needed
if self.scale :
X = self.scale_features(X)
# Initialize weights and bias
self.w = np.zeros(X.shape[1])
self.b = 0
for i in range(self.iterations):
z = X.dot(self.w) + self.b
# pred = np.where(z >= 0, 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z)), np.exp(z) / (1 + np.exp(z)))
pred = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
epsilon = 1e-8
pred = np.clip(pred, epsilon, 1 - epsilon)
error = pred - y
dw = (1/m) * np.dot(X.T , error)
db = (1/m) * np.sum(error)
# Update the weights and bias
self.w -= self.alpha * dw
self.b -= self.alpha * db
# Calculate and store the cost
cost = (-1/m) * np.sum(y * np.log(pred) + (1 - y) * np.log(1 - pred))
self.cost_history.append(cost)
def predict(self,X):
"""Make predictions using the trained model."""
if self.scale:
X = (X - self.mean) / self.std
logits = X.dot(self.w) + self.b
prob = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-logits))
return (prob >= 0.5).astype(int)
def predict_proba(self, X):
"""Return probability estimates for the positive class."""
if self.scale:
X = (X - self.mean) / self.std
logits = X.dot(self.w) + self.b
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-logits))
def get_cost_history(self):
return self.cost_history
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Initialize and train the model
model = LogisticRegression(alpha=0.1, iterations=1000, scale=True)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
cost_history = model.get_cost_history()
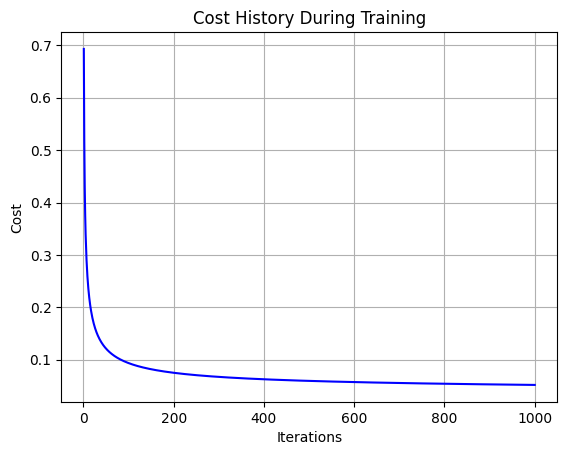
plt.plot(range(1, len(cost_history) + 1), cost_history, color='blue')
plt.title('Cost History During Training')
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
# Make predictions on all datasets
y_train_pred = model.predict(X_train)
y_test_pred = model.predict(X_test)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, roc_curve
train_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred)
test_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_test_pred)
print(f"Training Accuracy: {train_accuracy}")
print(f"Test Accuracy: {test_accuracy}")
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_test_pred)
print("Confusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
report = classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred)
print("Classification Report:")
print(report)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Training Accuracy: 0.9912087912087912
Test Accuracy: 0.9736842105263158
Confusion Matrix:
[[66 1]
[ 2 45]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.97 0.99 0.98 67
1.0 0.98 0.96 0.97 47
accuracy 0.97 114
macro avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 114
weighted avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 114
Logistic Regression using scikit-learn
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression as SklearnLogisticRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# Scale the features
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
# Initialize and train the sklearn logistic regression model
clf = SklearnLogisticRegression(random_state=42, solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000)
clf.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
# Make predictions on the training and test sets
y_train_pred_sklearn = clf.predict(X_train_scaled)
y_test_pred_sklearn = clf.predict(X_test_scaled)
# Evaluate the performance
train_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred_sklearn)
test_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_test_pred_sklearn)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_test_pred_sklearn)
class_report = classification_report(y_test, y_test_pred_sklearn)
print("Training Accuracy:", train_accuracy)
print("Test Accuracy:", test_accuracy)
print("Confusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
print("Classification Report:")
print(class_report)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Training Accuracy: 0.9934065934065934
Test Accuracy: 0.956140350877193
Confusion Matrix:
[[66 1]
[ 4 43]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.94 0.99 0.96 67
1.0 0.98 0.91 0.95 47
accuracy 0.96 114
macro avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 114
weighted avg 0.96 0.96 0.96 114
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.